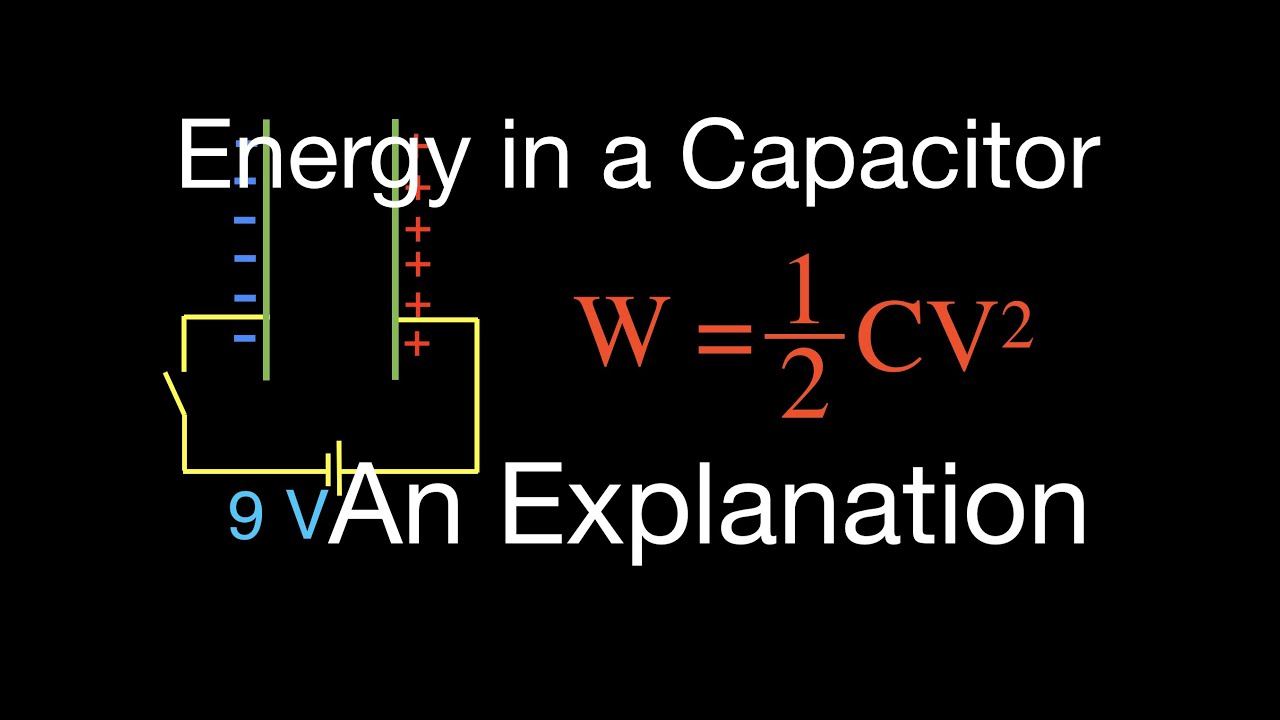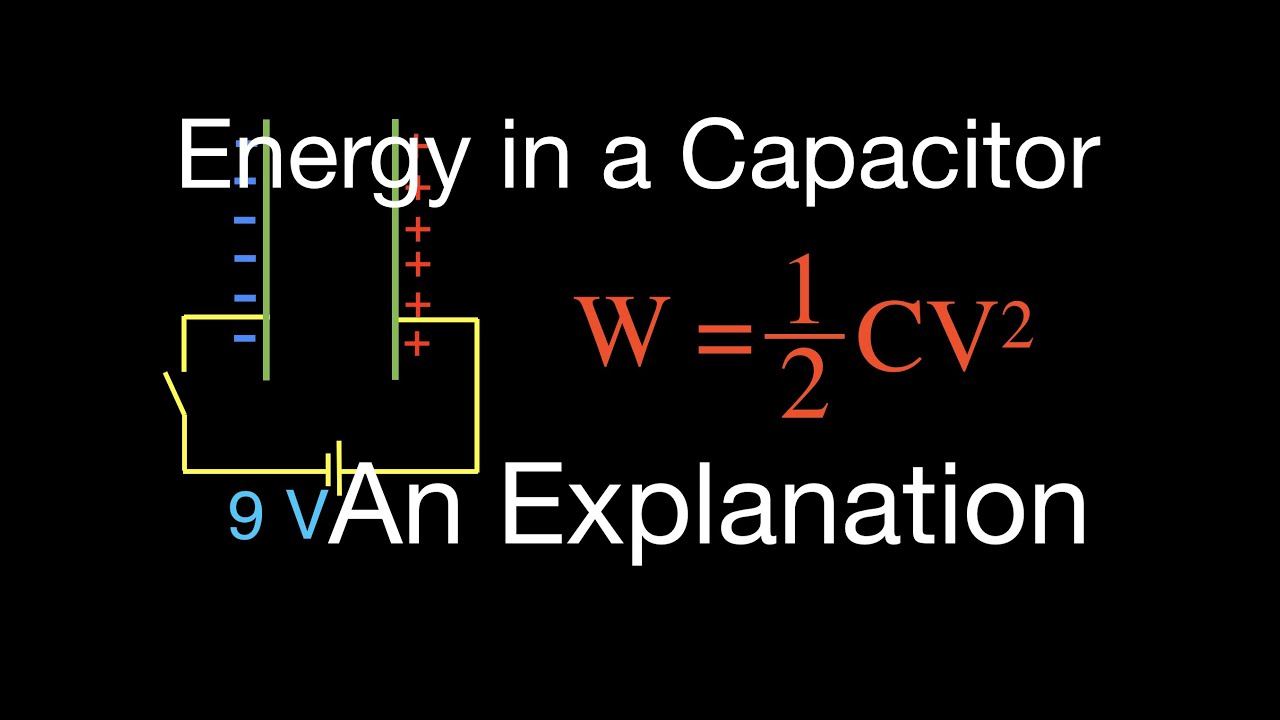The energy stored in a capacitor is given by the equation u frac 1 2 cv 2.
Capacitor stores energy in the form of electric field.
When the voltage is applied across a capacitor a certain amount of charge accumulates on the plates.
Definition of capacitor and battery while a battery stores its potential energy in the form of chemical reactions before converting it into electrical energy capacitors store potential energy in an electric field.
Capacitors are devices which are used to store electrical energy in a circuit.
Let us look at an example to better understand how to calculate the energy stored in a capacitor.
How a capacitor stores energy a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electric field that is established by the opposite charges on the two plates a capacitor obeys coulomb s law.
For example a resistor converts electrical energy to heat.
The total electric potential energy stored in a capacitor is given by.
Capacitor has equal magnitude of ve and ve charge.
A capacitor stores energy in the form of a electric field specifically electro static charge an inductor stores energy in the form of a magnetic field.
Energy stored on a capacitor.
This is known as the joule effect.
A force exists between two point source charges that is directly proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the.
A capacitor stores it in its electric field.
If the capacitance of a capacitor is 50 f charged to a potential of 100 v calculate the energy stored in it.
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field it is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
Some elements in a circuit can convert energy from one form to another.
The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance while some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit the capacitor was originally known as a condenser.
The electric potential energy stored in a charged capacitor is just equal to the amount of work required to charge it that is to separate opposite charges and place them on different conductors.