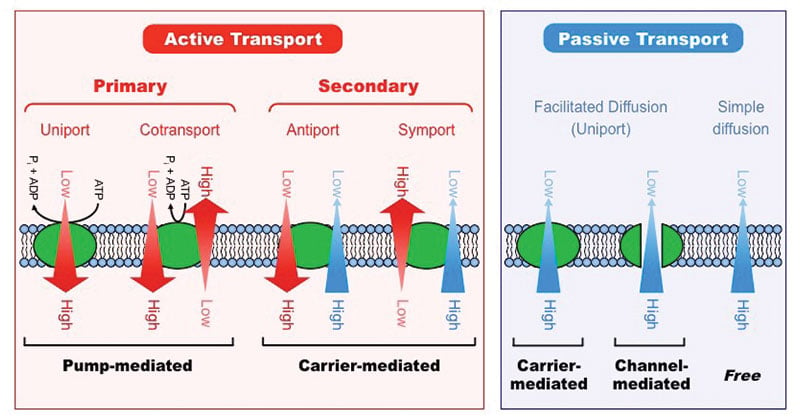
Secondary active transport involves the use of an electrochemical.
Carrier mediated transport that requires energy.
In carrier mediated transport both sides doors of carrier are not open at same time.
Types of carrier mediated transport can have passive transport facilitated transport facilitated diffusion which does not require energy can also have active transport.
Active transport occurs only through the lipid layer of the cell membrane where the transported substance combines with a specific carrier protein.
There are specific receptors on the membrane of carriers that recognize the target molecules and transport them across the cell.
This is usually to accumulate high concentrations of molecules that a cell needs such as glucose or amino acids.
Carrier mediated transport is an energy dependent pathway generally used by small hydrophilic molecules.
It requires energy derived directly from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate or another high energy phosphate compound creatine phosphate this leads to the conformational change in the carrier and it pumps the carried substance across the.
During active transport atp is required to move a substance across a membrane often with the help of protein carriers and usually against its concentration gradient.
Passive transport is a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input.
If the process uses chemical energy such as adenosine triphosphate atp it is called primary active transport.
Active transport is the movement of solutes against the electrochemical gradient which requires energy.
In order to sustain metabolism cells must take up glucose amino acids and other organic molecules from the extracellular environment.
Secondary energy for transport isn t provided directly by atp hydrolysis but by using existing gradient of an ion to drive transport sites for both ion and substance must be simultaneously occupied.
Active transport is the movement of a substance across a membrane against its concentration gradient.
Unlike active transport it does not require an input of cellular energy because it is instead driven by the tendency of the system to grow in entropy the rate of passive transport depends on the permeability of the cell membrane which in turn depends on the.
Carrier mediated transport that occurs against a concentration gradient and which therefore requires metabolic energy is called active transport.
Membrane proteins that aid in the passive transport of substances do so without the use of atp.
The kinetics of carrier transport are similar to the kinetics of enzyme mediated chemical reactions.
The direction of transport is reversible and is determined by the electrochemical gradient of the solute.
Protein carrier mediated transport against a gradient requires energy.